Skin Cancer Check
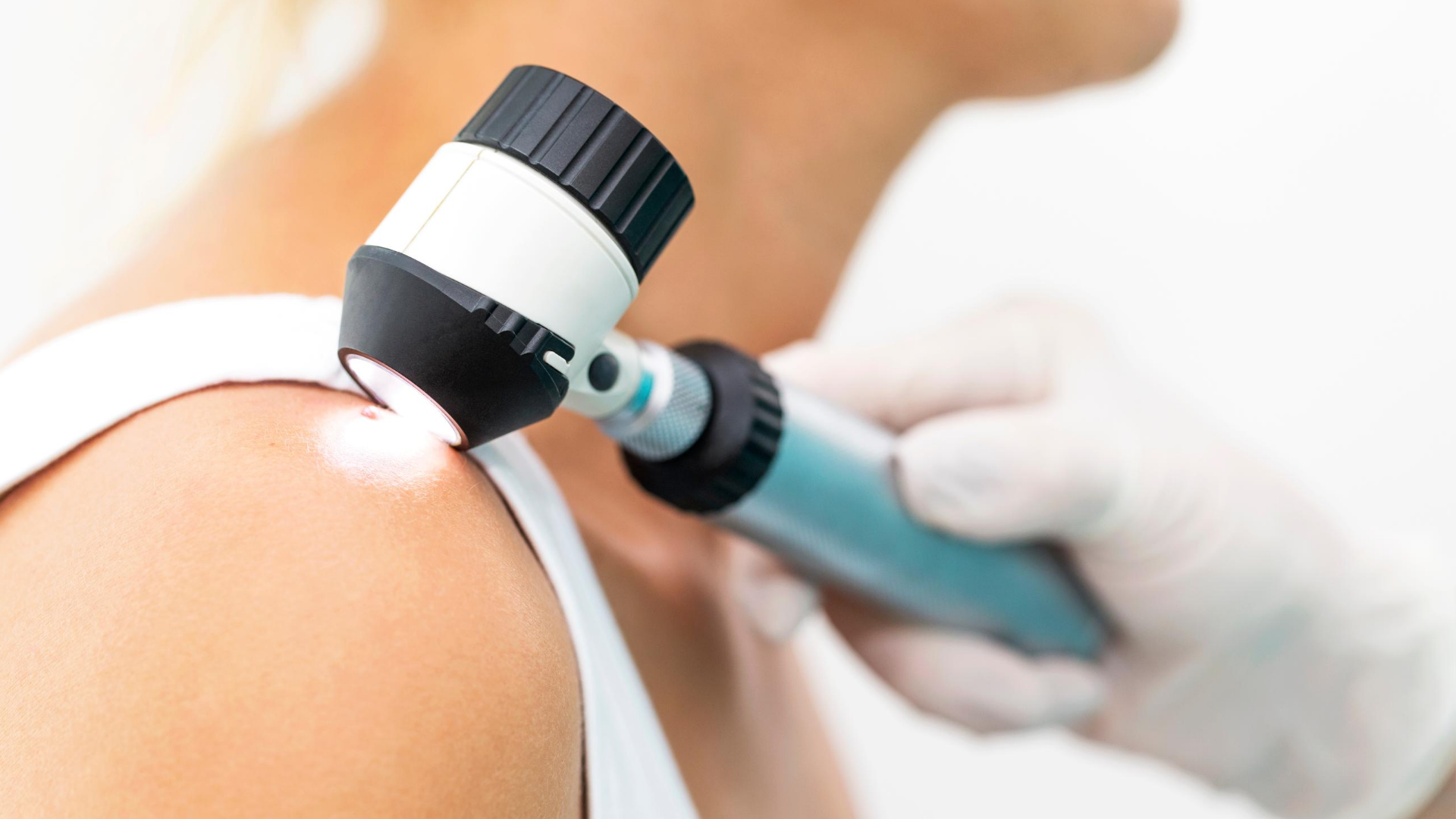
Skin Cancer Check
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world!
According to World Cancer Research Fund International, Australia had the highest rate of melanoma, followed by New Zealand. More than 2,000 Australians die from skin cancer each year.
Amtan Medical offers complete range of advanced, coordinated treatment services for all types of skin cancers. Amtan has qualified skin cancer specialists and surgeons and highly trained support staff.
Right from the application of novel imaging techniques to the usage of innovative chemoprevention trials, our team are dedicated to providing comprehensive care on your health journey.
Our Skin Cancer Specialist Team are available for bookings now across all of our 8 medical centres, or book for the best treatment professionals in one of our dedicated Skin Cancer Clinics today at:
- Ormeau Family Practice
- Ormeau Village
- Pimpama City
- Pimpama Junction
- Hope Island Marketplace
- Oxenford Village
- Pacific Pines
- Reedy Creek
Why is Amtan Medical leading in Skin Cancer treatments?
- Early detection mechanism
- Precise diagnosis and advanced treatment
- Advanced Skin Cancer Surgery performed
- Prevention services
- Regular and timely follow-up
- Highly trained and experienced staff
- Affordable treatment plans
Are you sure you know what Skin Cancer is?
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells are damaged – three main types of skin cancer are:
- basal cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma
- melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are known as non-melanoma skin cancer.
Exposure to the sun is the predominant reason for majority of skin cancers. Anyone can be at risk of developing skin cancer. However, people with pale skin types and older people are more vulnerable to the disease. The more sun you are exposed to, the higher the risk.
Early detection is the most important tool in the fight against skin cancer. Be vigilant and if you have any of the following, book today with an Amtan Skin Cancer Clinic:
- Spent lots of time in the sun, even if sunscreen is used
- Use tanning beds or solariums
- Have a family history of skin cancer
- Your skin is fair, burns easily and does not tan
Some of us have a lack of protective pigmentation which leaves our skin cells vulnerable to DNA-damaging rays from the sun. Australian’s have the opportunity to enjoy long hours of sunshine and its potential harmful rays – those that have fair skin are ill-suited to long term exposure.
Australia’s proximity to the equator further increases the amount of UV and the intensity of being exposed to the sun. Australia’s proximity to Antarctica, where the well documented ‘hole’ in the ozone layer increases our risk with the decreased protection from the Ozone filtering some of the harmful UV rays. Being closer to these influences is why Queensland reports much higher rates of skin cancer than any other state.
We must be constantly vigilant about the amount and intensity of sunlight that we get exposed to everyday.
UV RADIATION
95% of melanomas and 99% of non-melanomas are triggered by over-exposure to UV radiation. UVA penetrates deep into the skin and causes genetic damage to cells. UVB penetrates into the top layer of the skin and causes damage to the cells. If the body is unable to correct this damage, then cells begin to grow exponentially.
Statistics reveal that 1 in 8 adults and 1 in 5 teenagers are sunburnt on an average Australian summer weekend. Even if you don’t get burnt, exposure to sunlight can still cause damage to skin cells and increase risk of skin cancer.
Many carry the false notion that on cooler or cloudy days, you are protected from UV radiation. But the truth is that even if the temperature is cool, you are still at risk of sunburn.
The Golden Sunkissed skin – Having a TAN
On a sunny day, most of us flock to beaches for some good beach fun in the sun and the glowing sun kissed ‘healthy’ look from a tan. But, in reality, there is nothing healthy about a tan.
Tanning is a sign that you have been exposed to enough UV radiation to damage your skin to the point that there is a visible change in its colour as it tries to protect itself. Hard to believe when we are conditioned from early on to think a tan is ‘healthy’.
There are a lot of myths around the damage that UV rays can cause to our body, even some believing that getting a base tan using a tanning bed will help prevent sunburn. This does nothing to protect you from sunburn. Research has also proven that tanning beds are no safer than the sun.
Tanning essentially tells you to press the panic button!
OTHER CAUSES
Other less common causes for skin cancer are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
TREATMENT
Melanoma treatment can include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation or a combination. The most common and effective treatments for non-melanoma skin cancer are surgical.
PREVENTION
Since, the majority of skin cancers are related to sun exposure, it is preventable. Reducing sun exposure and early detection are the best defense.
The sun’s rays are the strongest between 10 am and 4pm. Protect your skin with clothing and sunscreens during this time. Sunscreen applied correctly and regularly can go a long way towards preventing sunburn. Make sure you use the right sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of at least 30. A broad-spectrum sunscreen means that the sunscreen protects you against both types of UV radiation – UVA and UVB. Apply sunscreen 15 minutes before sun exposure and regularly reapply, especially if you are swimming or it’s a hot day and you are sweating and then reapplying every two hours.

Comments (2)
Cheryl Evans
31 Aug 2020 - 6:35 pmIs there a cost involved?
Or is this bulk billed?
AMTAN BLOG
01 Sep 2020 - 10:39 amHi Cheryl,
Thanks for contacting us. The service is bulk billed.
Comments are closed.